CS log
Network Layer ; IPv6 & SDN 본문
지난 시간 배운 내용
end-to-end로 보낸 message가 layer 3에서 host를 찾아가는 것을 focusing하고 있음.
destination host를 찾아가야 해서 IP주소를 넣었음. 중간 라우터들이 IP주소를 보고 FIB table에서 matching해서 찾을 때, longest prefix matching: 가장 길게 완벽히 match되는 것이 entry에 있으면 그것으로 했음.
여러 개의 subnet을 구성하고 있는 (/28) 하위 subnet들은 상위 ISP에게 알려줄 때, /26까지 aggregation해서 하나만 알려주면 된다. 가능하면 적은 양의 데이터로 라우팅 하는 것이 좋기 때문에.
subnet 중 어느 하나가 다른 network로 이사가더라도, longest prefix matching을 사용하기 때문에, 추가로 갖고 있는 routing entry를 가지고 있으면 된다.
CIDR을 썼음에도 public 주소가 너무 고갈 되니까, 너도 나도 쓸 수 있게 private 주소를 사용. 내 라우터에 NAT 혹은 NAPT 기능을 enable 시켜 여러 private 주소에 하나의 public IP 주소만 할당 되도록 함.
Pop Quiz
NAT 기능이 있는 router에서는 layer 4계층의 port정보를 조작할 수 있다.
⇒ T. router는 3계층까지만 control해야 하는데 그 rule을 깬 것이 NAT. 4계층의 port번호를 조작하기도 함.
NAT의 단점?
⇒ private network에서 먼저 connection을 initiate 하는 경우엔 문제가 없으나, private network에 있는 server에 public client가 들어오는 경우, 접근을 할 수 없음.
solution )
- relay 방법은 peer들 사이의 중계 역할을 하여 마치 client에게는 server인 것 처럼, server에게는 client인 것처럼 대응해주어 모든 packet을 relaying 시켜줌.
- connection reversal 방법은 Peer C가 Client에게 먼저 connection을 열라고 상대의 IP번호를 주어 중계만 해주면 Client가 initiate하여 통신할 수 있음.
Solution)
At Step 1: source address of the IP datagram: 10.0.1.21
destination address of the IP datagram: 128.119.168.188
source port number for the TCP segment of the IP datagram:3376
destination port number for the TCP segment of the IP datagram: 80
Host 10.0.0.13 has assigned an arbitrary source port number 3376 and sends thedatagram to LAN. The datagram is received at the NAT router's right port.
At Step 2: source address of the IP datagram: 135.122.193.218
destination address of the IP datagram: 128.119.168.188
source port number for the TCP segment of the IP datagram:5116
destination port number for the TCP segment of the IP datagram:80After receiving the datagram from host 10.0.0.13, the NAT router generates anew source port number 5116 (not already in use within the NAT table) for thedatagram and replaces the original source port number 3376 with the new sourceport number 5116. The traffic leaving the home router for the larger internethas the source IP of the NAT router which is 135.122.193.218, and thus thedatagram's source IP address now changes to 135.122.193.218. The destinationaddress and the port number remain the same. The NAT table, after step 2, lookslike (see Figure 4.25 in text):
WAN-side address : 135.122.193.218, 5116
LAN-side address : 10.0.1.21, 3376
At Step 3: source address of the IP datagram: 128.119.168.188
destination address of the IP datagram: 135.122.193.218source port number for the TCP segment in the IP datagram:80 destination port number for the TCP segment in the IP datagram:5116This arriving datagram was sent by remote host 128.119.168.188 in response tothe datagram sent by this NAT router in Step 2 above.
At Step 4: source address of the IP datagram: 128.119.168.188
destination address of the IP datagram: 10.0.1.21source port number for the TCP segment of the IP datagram: 80destination port number for the TCP segment of the IP datagram: 3376When this datagram arrived at NAT router's left port from the Internet, therouter indexed the NAT translation table using the destination IP address anddestination port number to obtain the appropriate IP address(10.0.1.21) anddestination port (3376) for the destination host in the home network. Therouter then rewrites the datagram's destination address and destination port number,andforwards the datagram into the home network.
IPv6
IPv4와의 차이를 아는 것이 중요.
Pop Quiz
IPv4 헤더에 있는 checksum은 Payload에 있는 전체 field에 대해 integrity check를 한다.
⇒ F. IPv4 헤더에 있는 checksum 필드의 이름은 headerCheckSum. header에 대해서만 checksum을 수행. Payload에 대해서는 하지 않음.
IPv4 router가 fragmented된 패킷을 assembly한다.
⇒ F. router에서는 assembly하지 않고, host에서 수행.
initial motivation: speed processing/ forwarding
IPv6가 생겨날 때 쯔음 fiber optic이 발달하며 error rate이 줄어들어 checksum field를 없애 버림.
IP fragmentation도 수행하지 않음. outlink bandwidth가 작을 경우 drop 하고 ICMP로 송신자에게 report.
no fragmentation allowed at router but enabled at host (host는 IPv6도 fragmentation을 수행)
IPv6 addressing (x:x:x:x:x:x:x:x, x = 16 bits)
128-bit address is represented as 16-bit hexadecimal fields(0-F) separated by colons.
IPv4와 다르게, NIC 하나에 여러 개의 IPv6 addresses들이 할당될 수 있다.
unlike IPv4, multiple IPv6 addresses can be allocated to one NIC card.
IPv6 datagram format
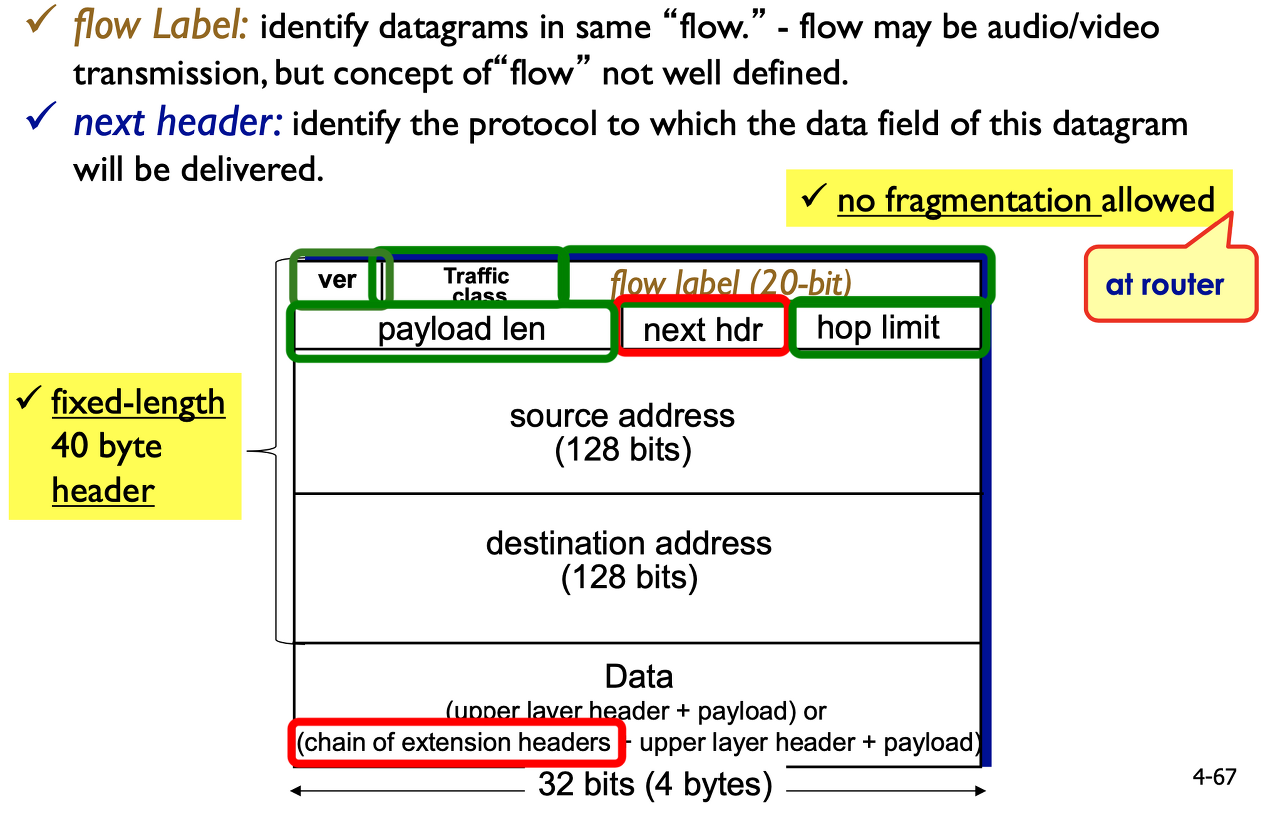
IPv4의 fixed 되지 않은 20 byte헤더와 달리 IPv6는 fixed된 40 byte 헤더를 가짐. 그리고 physical link = 빨라짐. 근데 QoS 망함
주소가 길어진 것이지 기능은 더 줄어듦. (128 bits src addr, dest addr = 16 byte + 16 byte = 32 byte)
flow label: e2e 흐름. 20 bit할당. 패킷들의 flow를 조절하려고 함. 실패
next hdr: data field에 another header가 들어올 수 있음. (header를 가리키고 이어져 extension 가능)
hop limit: ghost traffic을 잡는 TimeToLive와 같음.
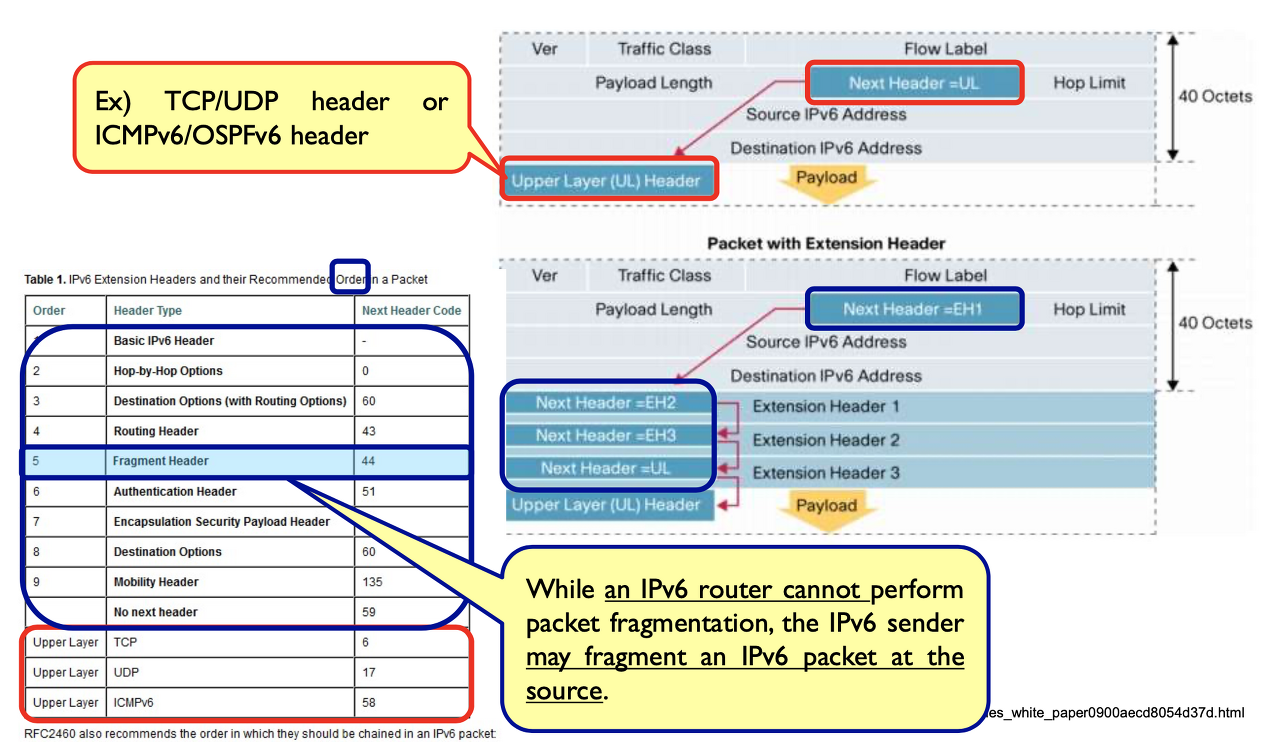
Chaining Extension Headers in IPv6 Packets - payload 안에 헤더가?!?!
data field에 있는 것이 다른 protocol의 메시지가 아니라 또다른 IPv6 header일 수 있음.
IPv6의 경우 헤더가 40 바이트로 고정되고 추가로 쓰고 싶은 건 payload에 넣어둔다. 필요할 때 쓴다.
extension header&chaining : 마지막 header가 상위계층을 가리킨다.
(tcp, udp) -> v6용으로 바꿀 필요는 없다. 왜냐하면 이들은 버전이 없기 때문에
pop quiz
IPv4 payload에는 TCP, UDP만 있다.
-> (x) raw sckt도 존재할 수 있다.
IPv6 payload에는 타 protocol도 들어가있다. (x)
IPv4 vs. IPv6
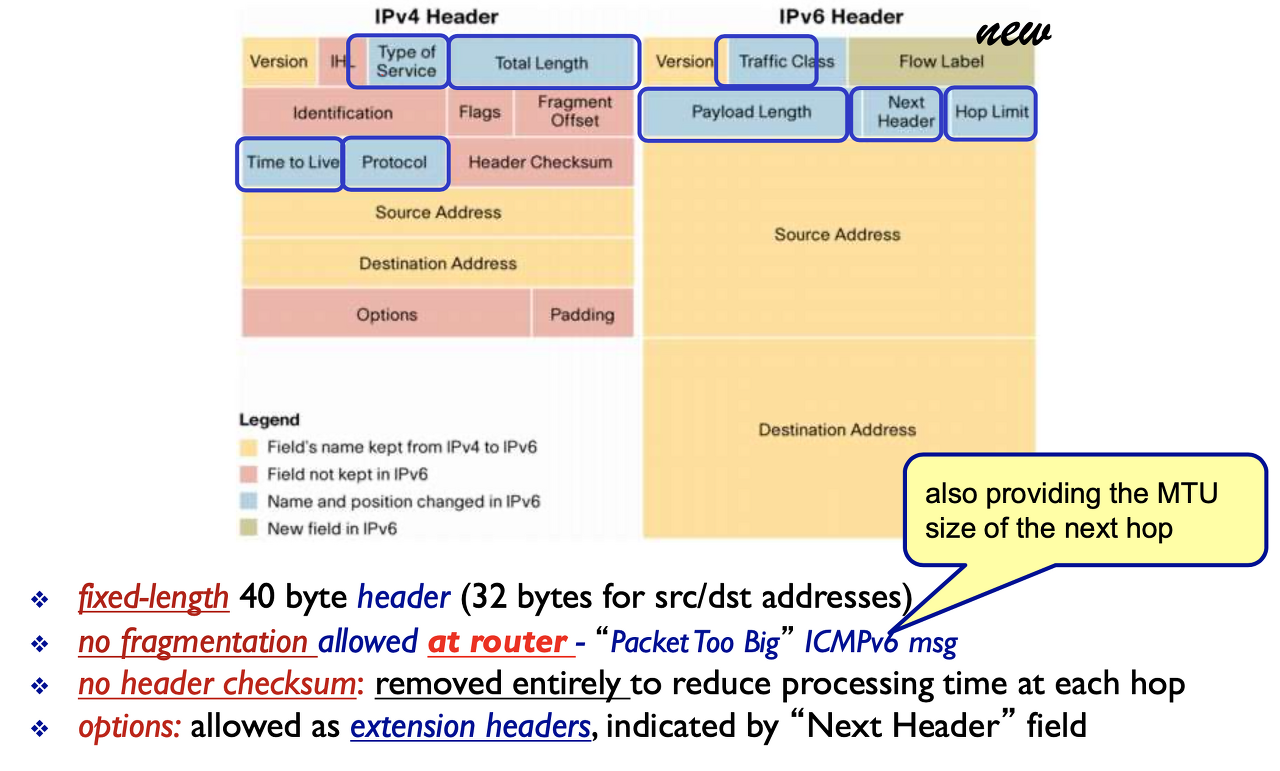
그림에서 노란색 = 그대로 남아있음, 빨간색 = 없어짐, 파란색 = 이름만 바뀜, 초록색 = new in IPv6
- <삭제된 부분>
- Option과 padding이 없어짐.
- header가 고정되어 있으니 header length 필요 없음. (버전만 확인하고 40 byte 확 읽으면 됨)
- host에선 해도 router에서는 fragmentation 하지 않으니 frag 필드 필요 없음 (id, flags, offset) ; 너무 크면 버리고 icmp한테 메세지를 보냄
- 고품질로 발전되어 링크가 error이 거의 없으니 checksum 필드 뺐음.
- <바뀐 부분>
- Time to live → Hop limit
- Type of Service → Traffic Class
- Total length → Payload length
- Upper layer Protocol → next header
Transition from IPv4 to IPv6
pop quiz :
URL만 안다. IPv4,6 둘다 되는 host. 어떤 version의 pkt을 보낼지 어떻게 아는가?
-> 돌아오는 답 (v4,v6) 보고 결정!
어떻게 network가 IPv4와 IPv6 모두에게 작동하도록 만들까?
Dual Stack
router가 하나의 interface에 두 주소를 모두 setting.NAT-PT (NAT-protocl translation)
protocol translation btw. IPv4, IPv6. (Payload 안의 주소도 필요시 바꿔줘야 함)- Tunneling !!!
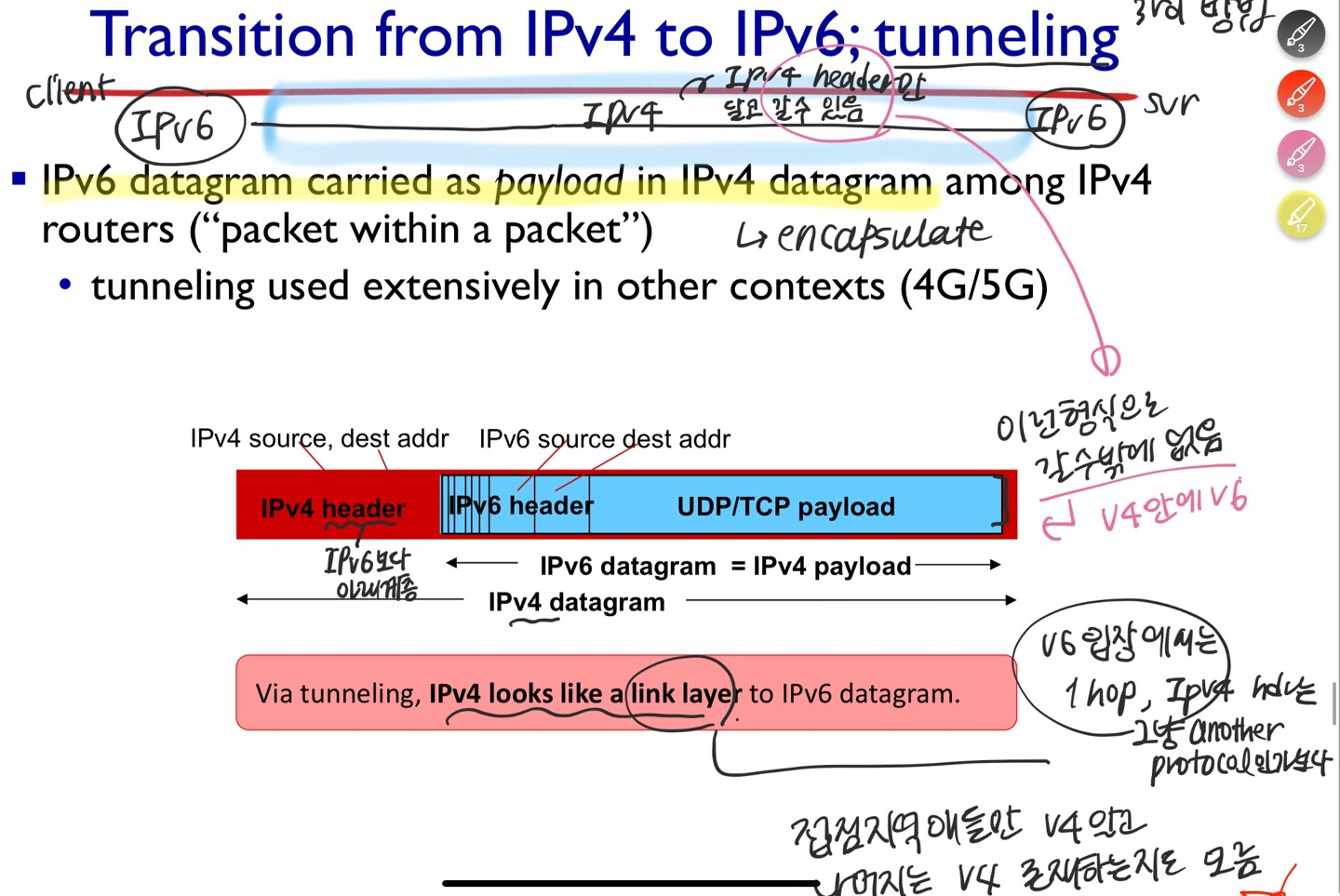
IPv6 datagram carried as payload in IPv4 datagram
v6 입장에서는 1hop을 가는건데, v4 헤더 입장에서는 그냥 another protocol인가보다~
<img width="1021" alt="스크린샷 2020-12-13 오전 12 45 25" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/45806836/101988370-7f3b5a80-3cdc-11eb-972d-0d1f03a0ecad.png">
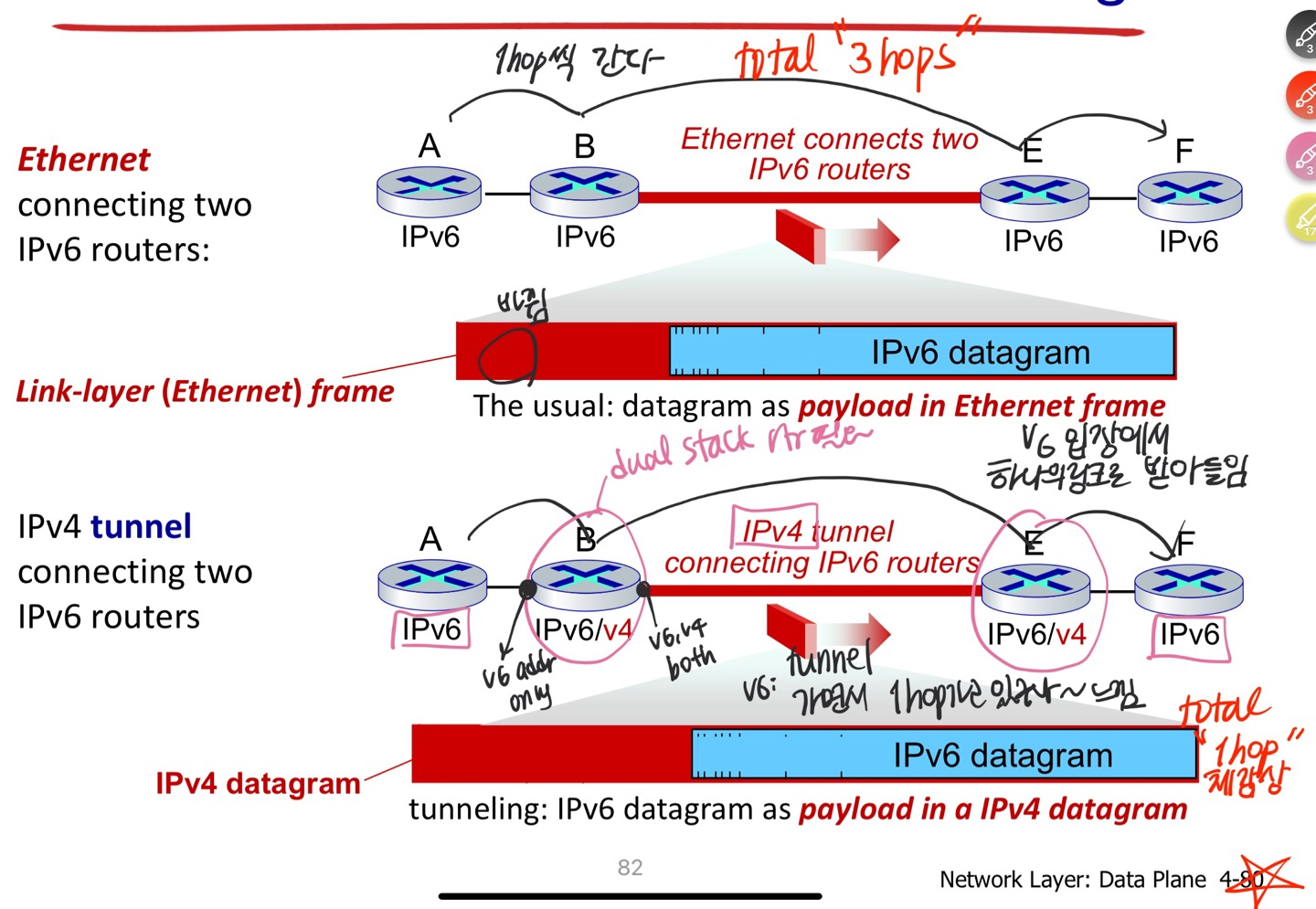
IPv6의 datagram을 IPv4 datagram 안의 Payload에 encapsulate. 마치 Layer2 frame처럼.
<img width="984" alt="스크린샷 2020-12-13 오전 12 46 54" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/45806836/101988411-b3af1680-3cdc-11eb-9bad-64660eeb4849.png">
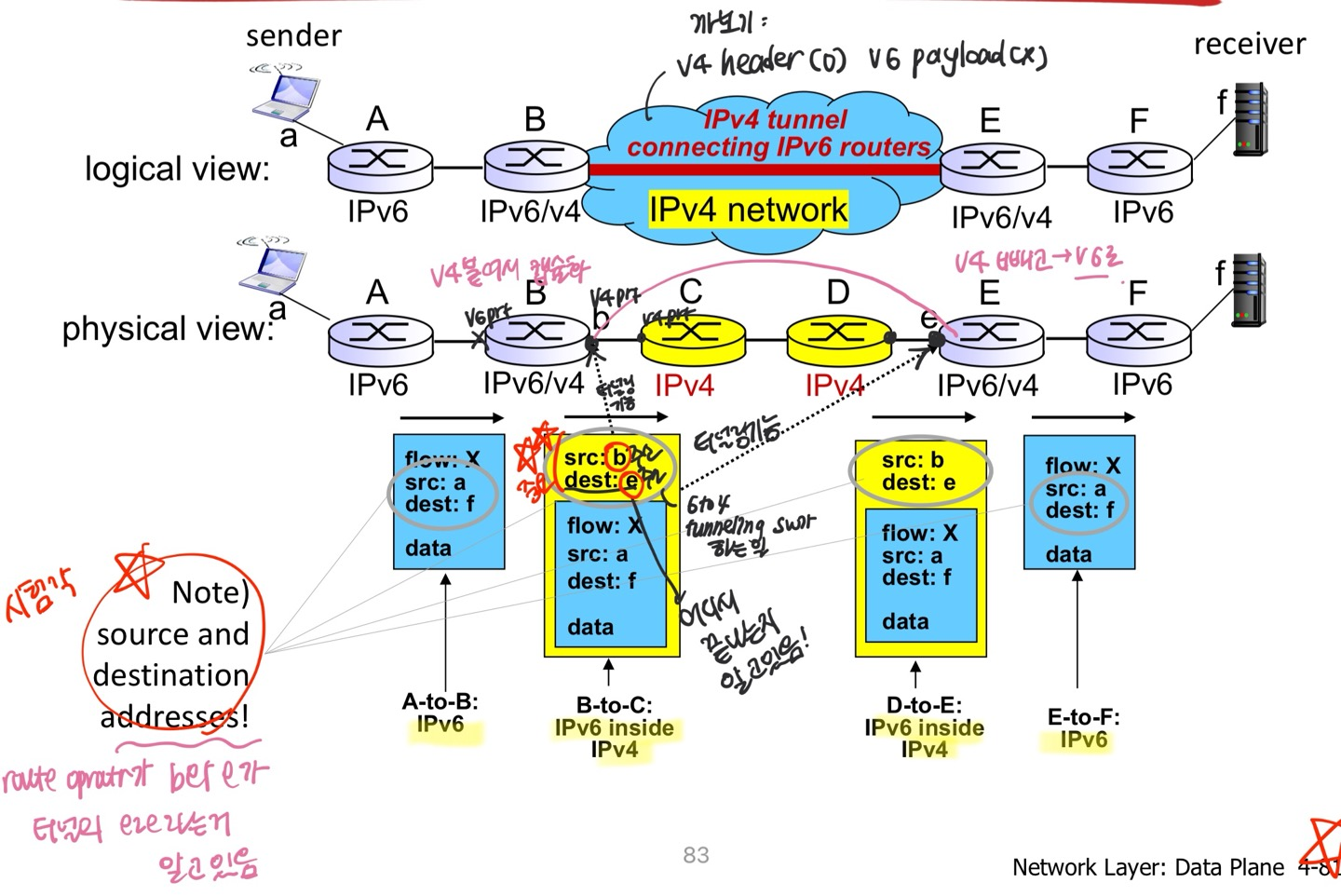
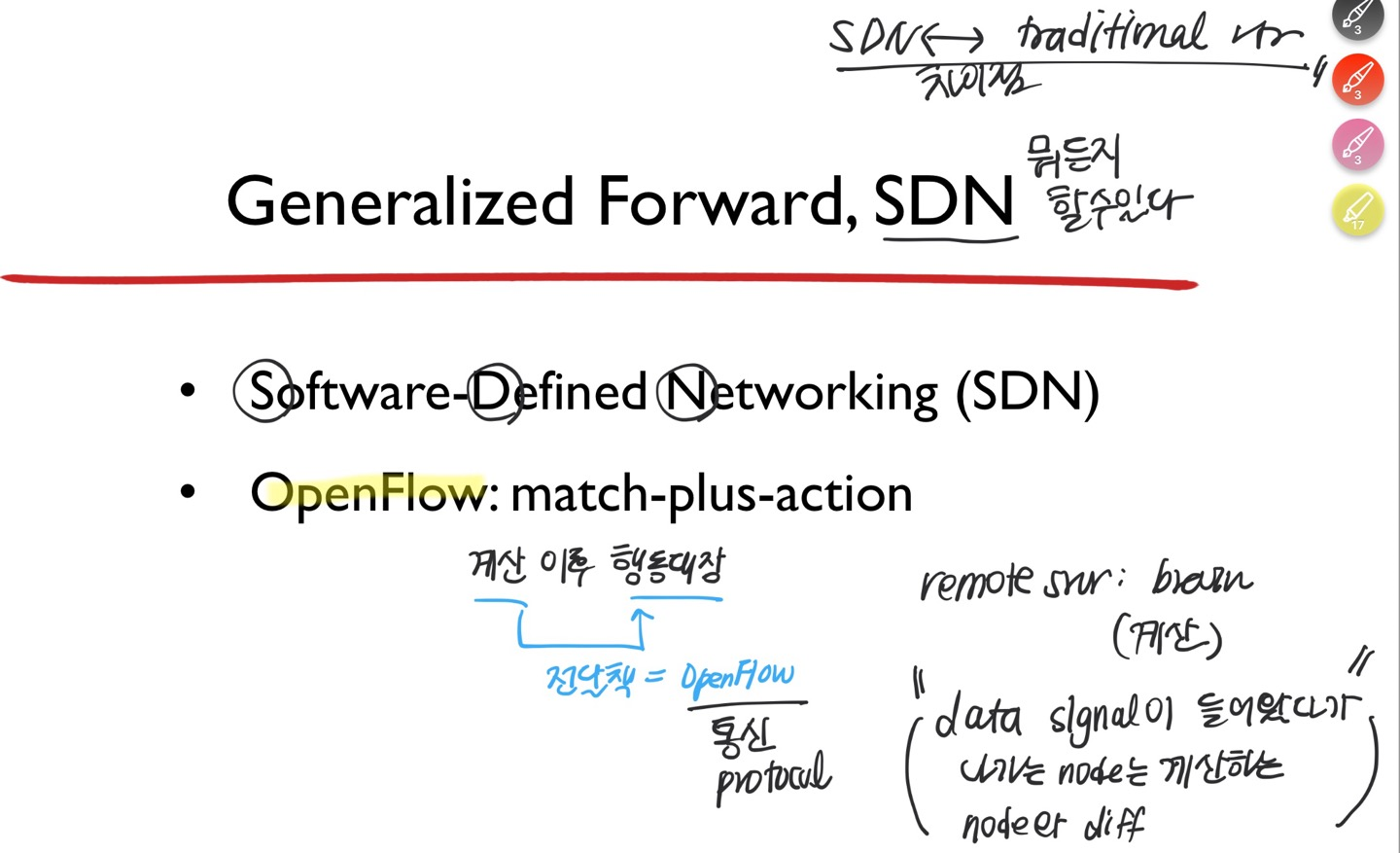
IPv4 Payload = IPv6 Packet, 접목하는 지점에는 어쨌든 Dual stack이 필요함. IPv4를 터널처럼 지나감.4.4 Generalized Forward and SDN (sdn은 뭐든지 할 수 있다! = complexity가 엄청 높다 )
- routing protocol은 한 가지 일만 한다. destination based forwarding을 어디로 할지 결정.
- router들은 서로 정보를 주고 받을 뿐이지, path selection 알고리즘도 각각의 라우터에서 running.
- 중앙에서 router들을 모두 보고 forwarding + a의 제어를 할 수 있다면? (기존 라우터의 middleware 기능)
Generalized Forwarding, SDN (Software-Defined Network)
Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
- 버전 4에서 안되었던 것들이 모두 가능하다!
- 특정 소스에서 destination 가는 path (e2e)를 정해진 루트로 보낼 수 없었음 ⇒ SDN은 라우터 이렇게 이렇게 거쳐가라! 라는 게 가능함 + 특정 src IP만 그 길로 가게 하겠어! 도 가능함
- 중간에 라우터가 있는데, 그 라우터에 들어오는 IP 중 특정 destination (subnet mask)인 애는 drop 하겠다 == IPv4에서 firewall 기능을 그냥 쓸 수 있음
- NAT 기능도 그냥 넣어버림
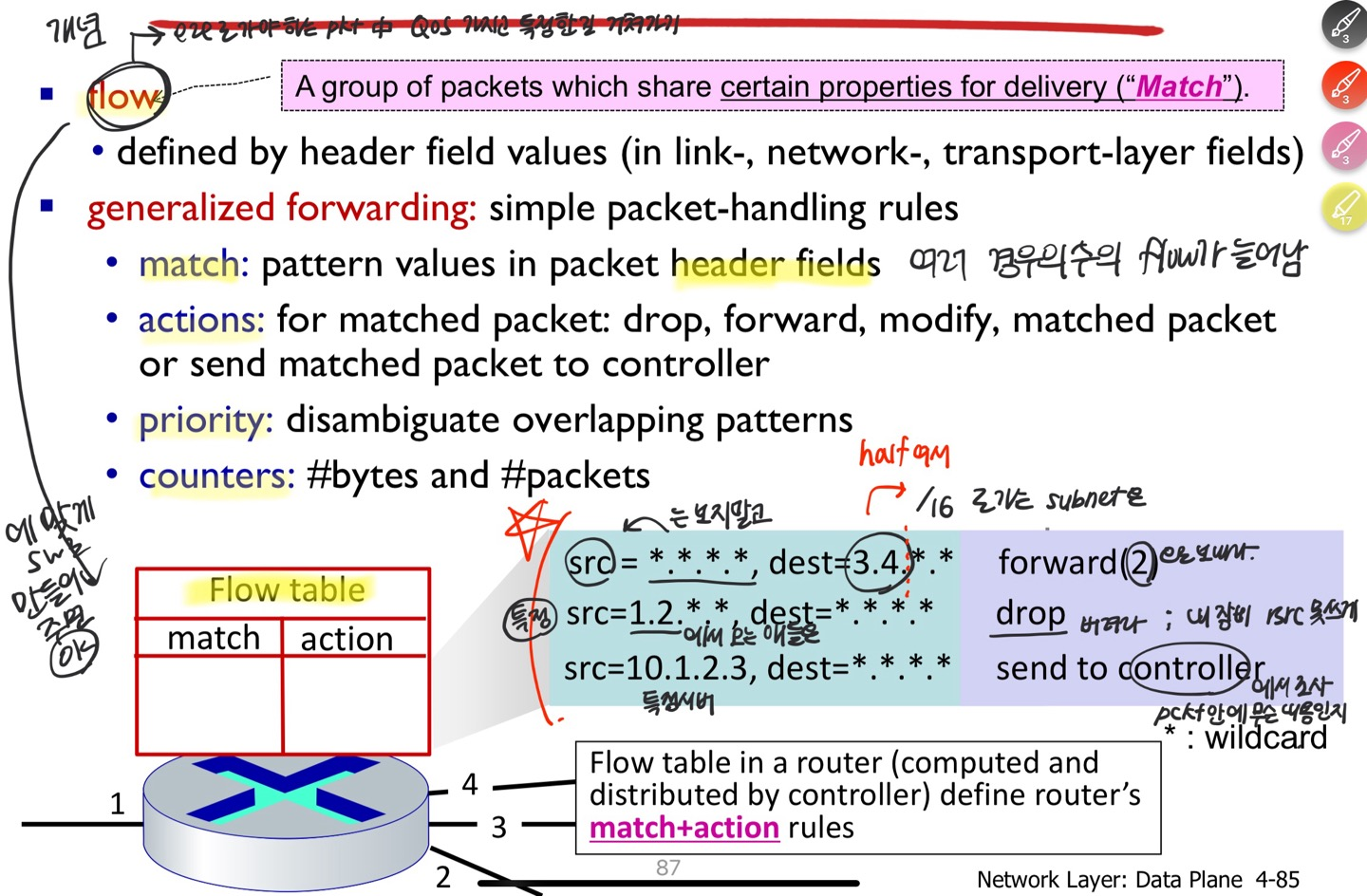
- ⭐ Generalized forwarding in SDN networks : more general match + action
- match : 2,3,4 layer headers
- action : load balancing, replacing address & port, selective dropping, deep inspection(점검), etc as well as forwarding
OpenFlow: match-plus-action
Generalized Forwarding : Match plus action
- Match plus action abstraction
- match bits in arriving packet, take action
- 도착한 packet의 어떤 layer의 header 값이든 bit를 match하고, action을 취한다
- destination-based forwarding
- forward based on dest IP address
- generalized forwarding
- many header fields can determine action
- many action possible : drop/copy/modify/log packet + control center로 보내라 -> 보내서 검사 후 재판단
- flow table : 계산 후 어떤 액션을 취할 지 정리되어있는 표
-

- match bits in arriving packet, take action
Flow table abstraction
Open flow
: SDN에서 사용하는 오픈 소스, 통신 프로토콜, 계산 이후 결과를 전달하는 행동대장
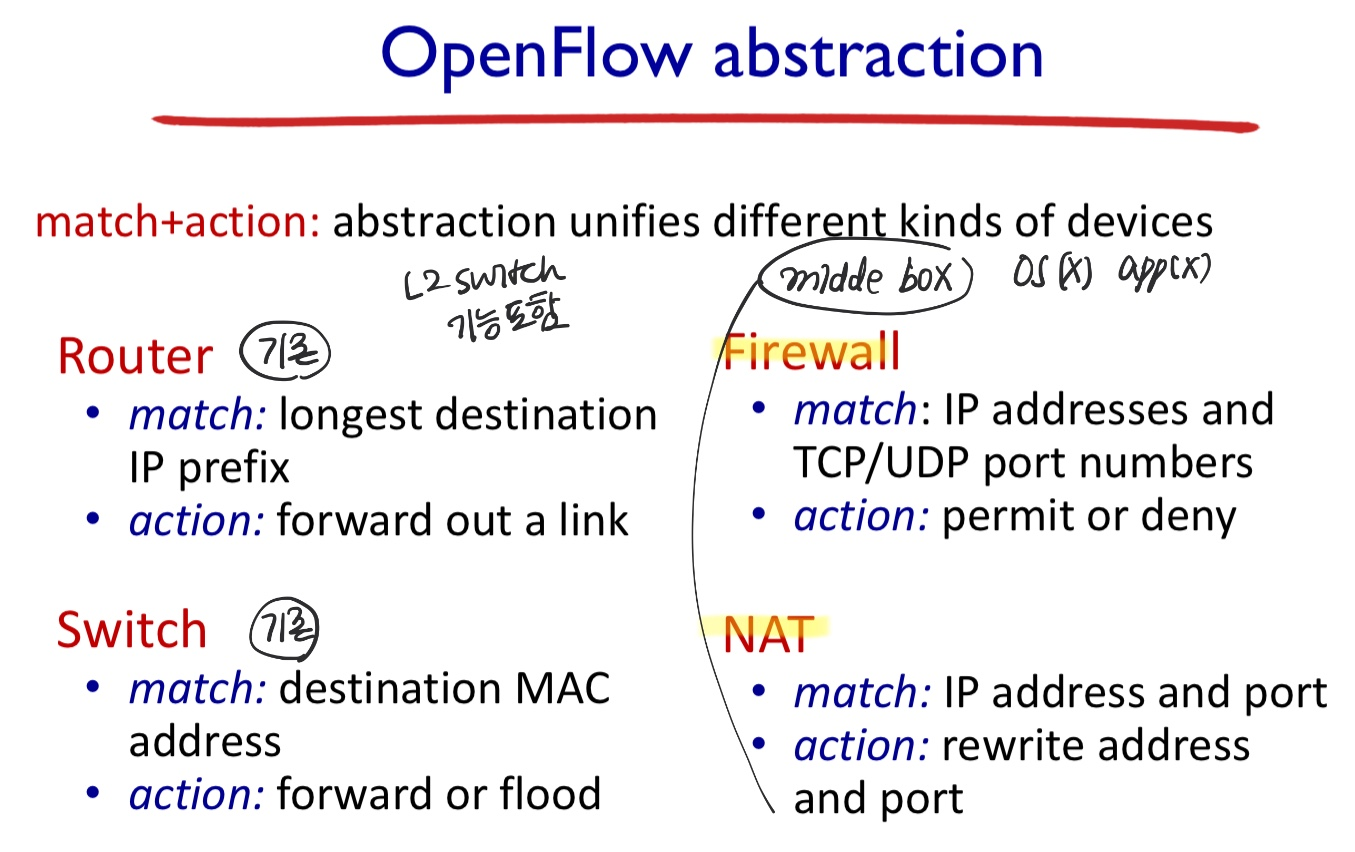
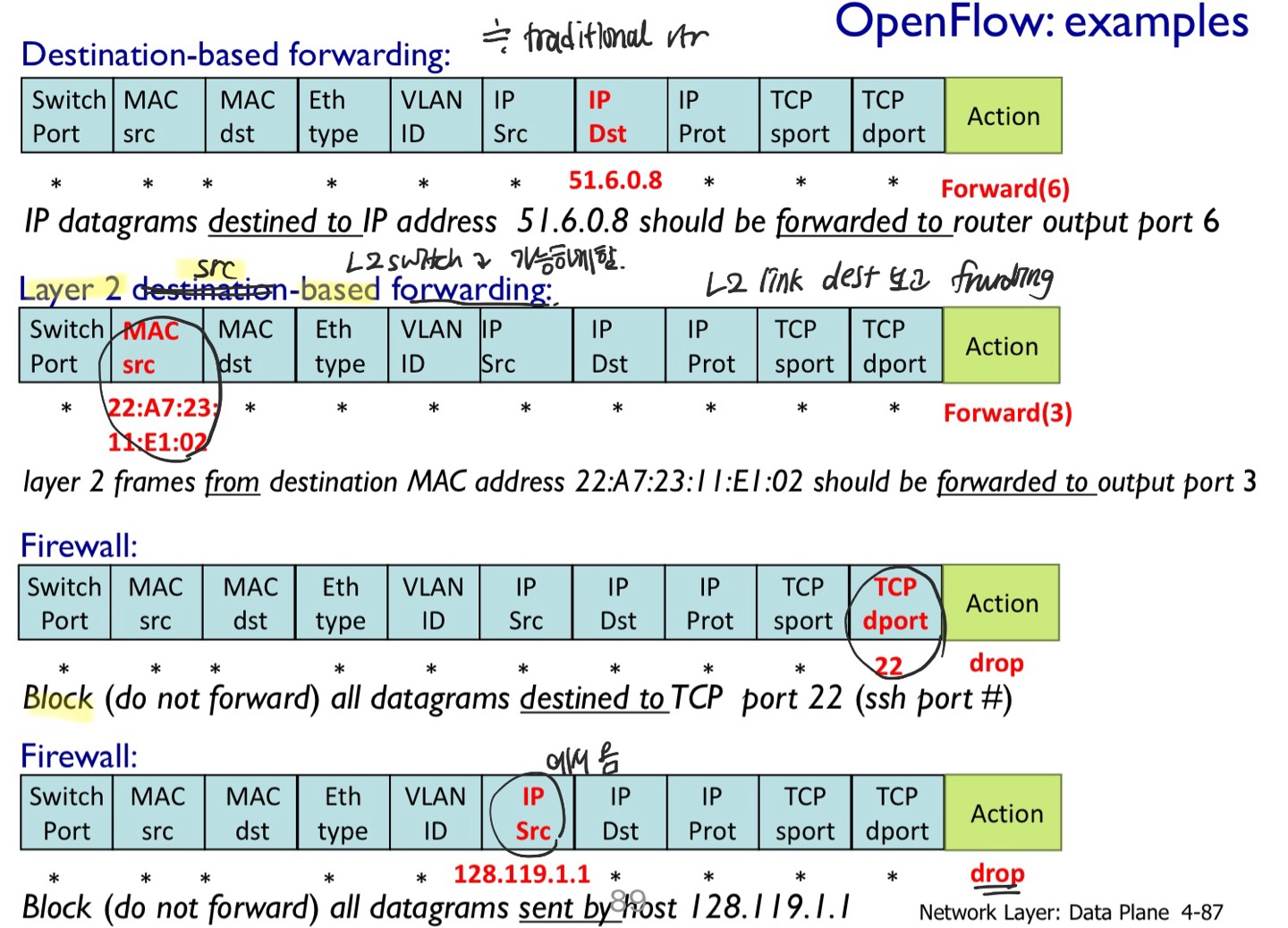
- 예전에는 Middlebox가 필요했던 것과 달리, 다 포함이 됨
- L2, L3, L4 장비 기능을 다 가지고 있음
예시1)
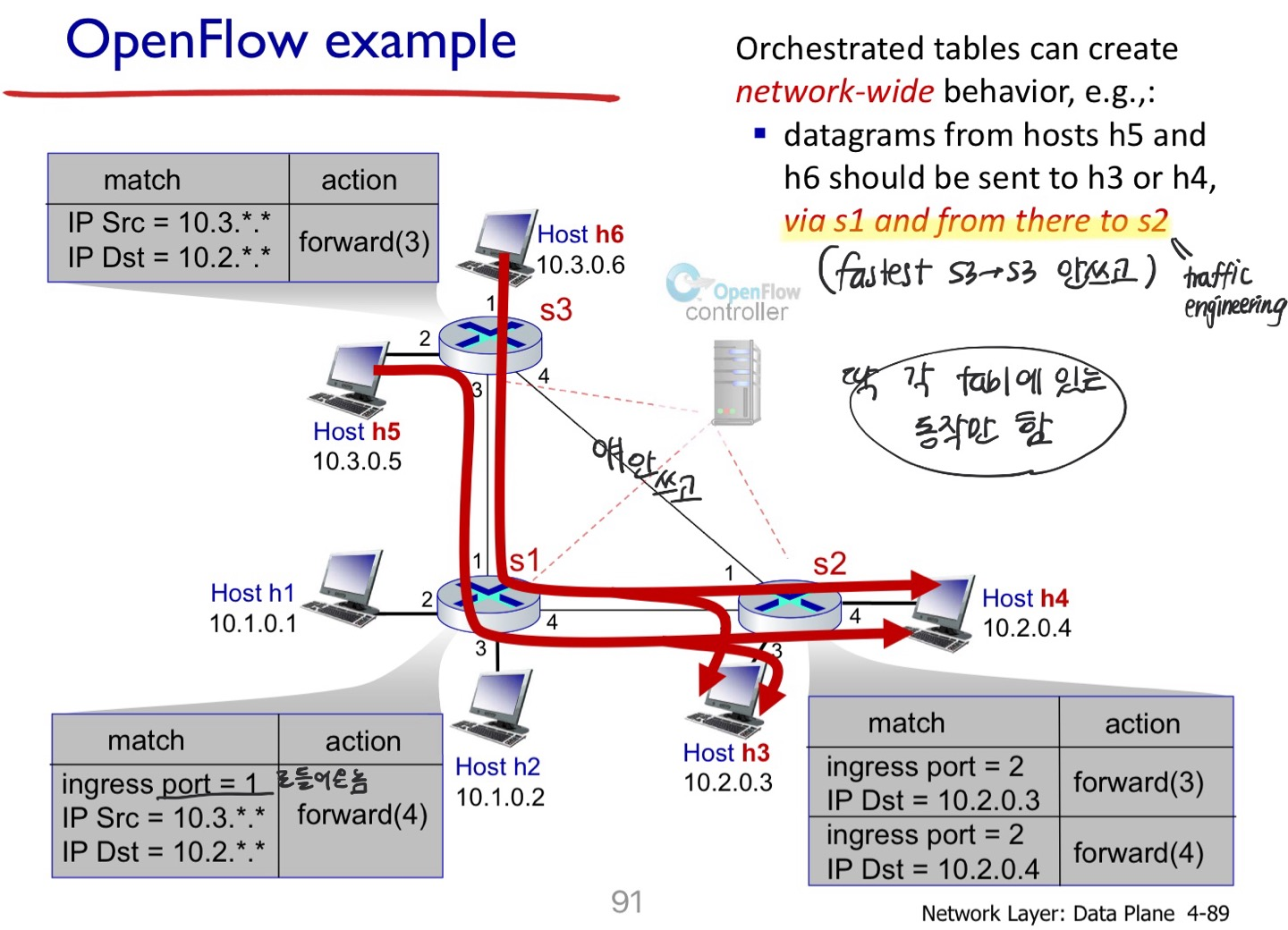
- Traditional 방식으로는 라우팅할 때 가장 짧은 길을 고르고, 하나만 고름(s3 → s2)
- 원래 길이 고장나지 않는 이상 돌아가는 길을 찾을 수 없음 (s3 → s1 → s2)
- 하지만 SDN은 뭐든지 가능함
- 트래픽을 어디로든지 지정할 수 있음. 정확하게 지정을 해버림
- 셋팅하는 건 Brain이 해주고, open flow한테 알려줌
예시2) load balancing
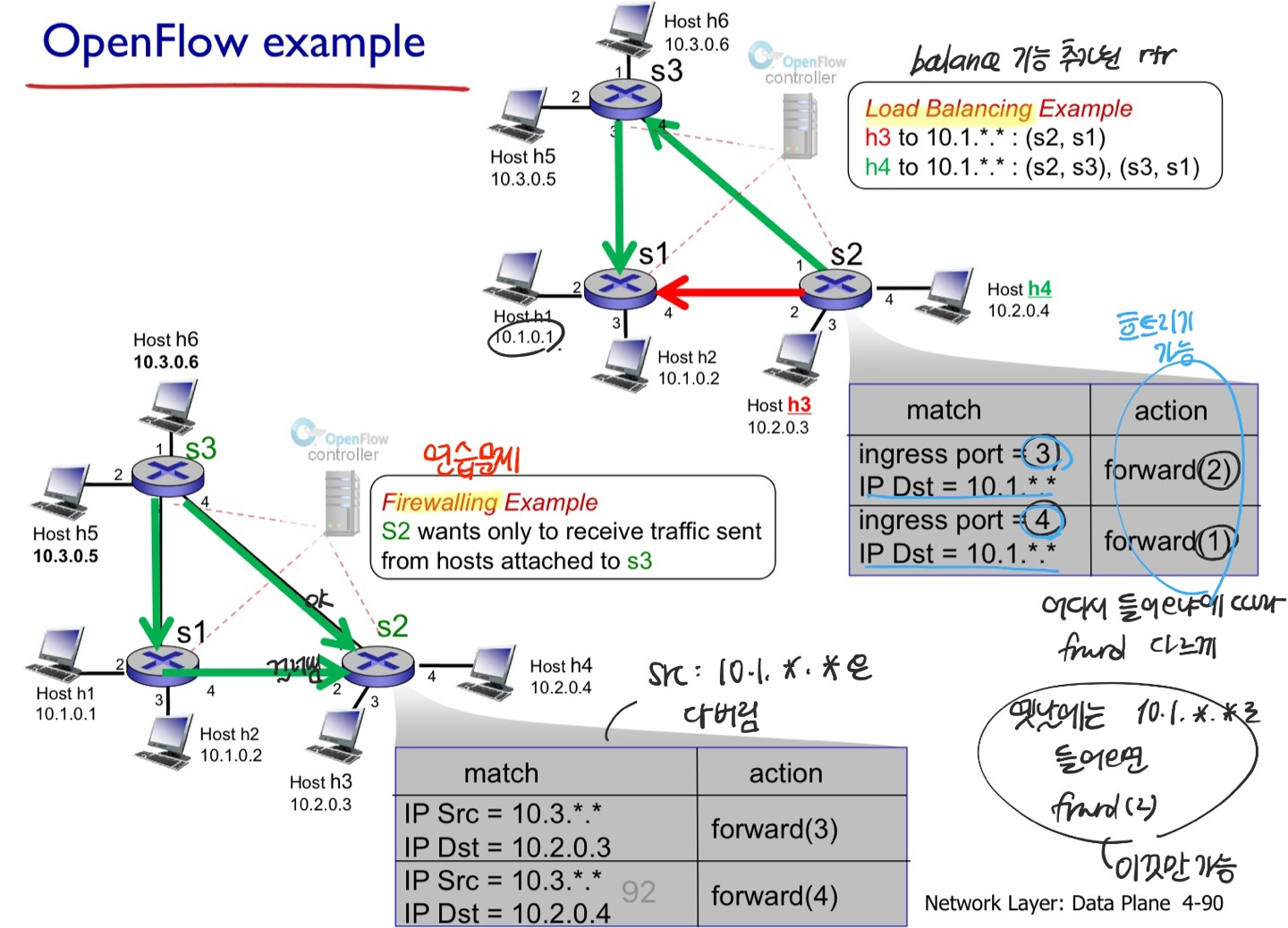
load balancing : traditional 방식에는 로드 밸런싱도 하지 못했지만, 여기서는 트래픽을 나눠줄 수 있으므로 로드 밸런싱 가능
firewall :
- s2 wants only to receive traffic sent from hosts attached to s3(s2는 s3에서 보낸 것만 받고 싶음)
- src가 아예 다른 s3에서 온다면 drop
- 정확하게 src 정해버린 케이스
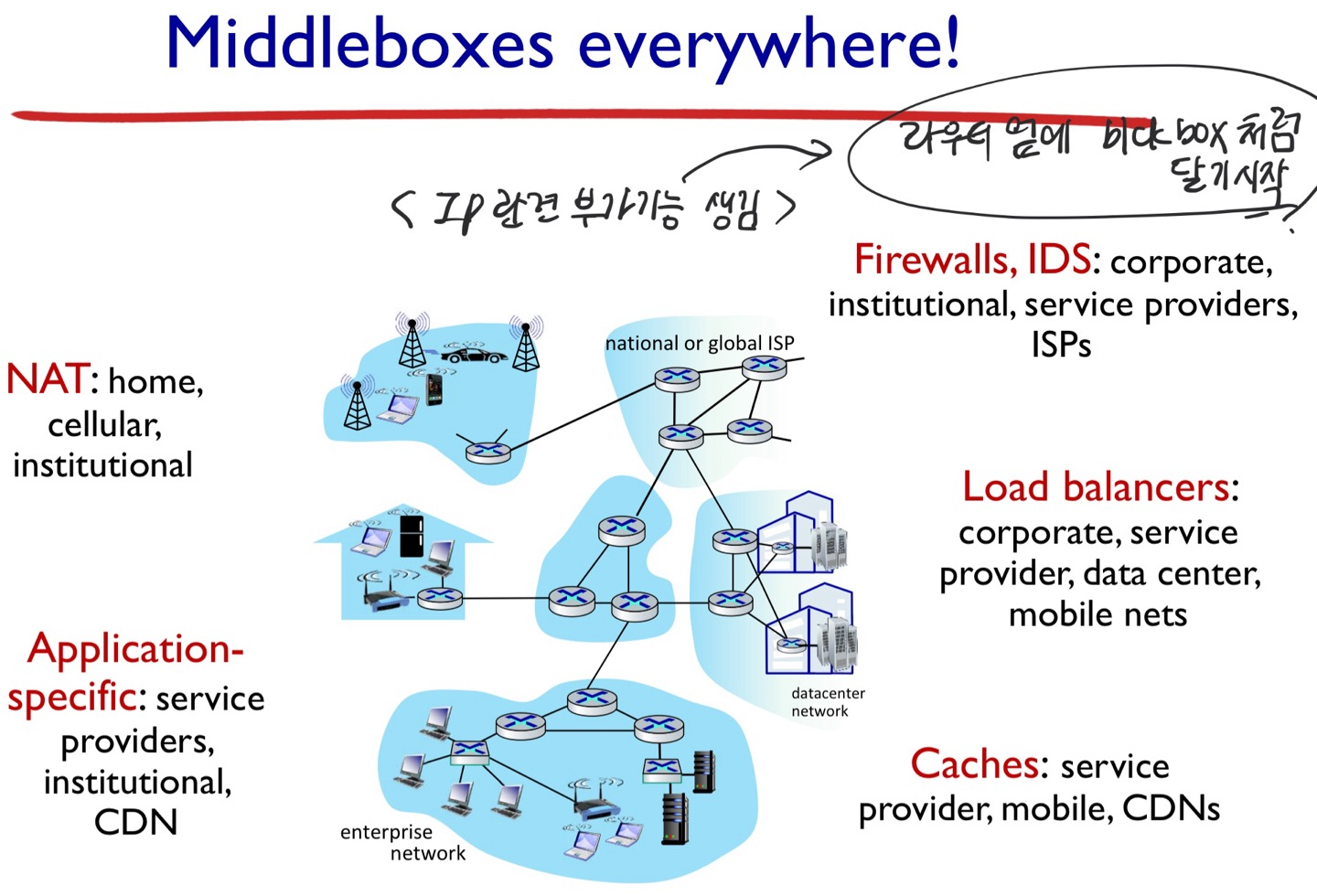
Middlebox
Any intermediary box performing functions apart from normal, standard functions of an IP router on the data path between a source host and destination host
src 호스트와 dst 호스트 사이의 데이터 경로에서 IP 라우터의 정상적인 표준 기능 이외의 기능을 수행하는 모든 중개 상자
- Principle of the early Internet
- Connectivity
- 다른 ISP을 엮을 때 최소한을 연결해라
- Internet Protocol (connectionless & best-effort service) at all layer 3
- 1)을 위해 IP는 connectionless + best effort service였음
- connectionless: 비연결성은 클라이언트가 서버에 요청을 하고 응답을 받으면 바로 TCP/IP 연결을 끊어 연결을 유지 하지 않는 것
- best effort service: 빠른 시간 내의 데이터 전송을 최우선으로 하는 전달 방식
- 가능한 내 위에 있는 애들한테 해주지 말고 그냥 단순히 연결해주는 역할을 해라! 앞뒤 상황 고려하지 말고
- 1)을 위해 IP는 connectionless + best effort service였음
- Intelligence at edges (complexity in smart hosts, programmable)
- 똑똑한 호스트가 있기 때문에 IP는 그냥 포워딩만 해주는 기능만 하면 됨
- Connectivity
다시 말해 원래 IP의 기능은 forwarding이였음
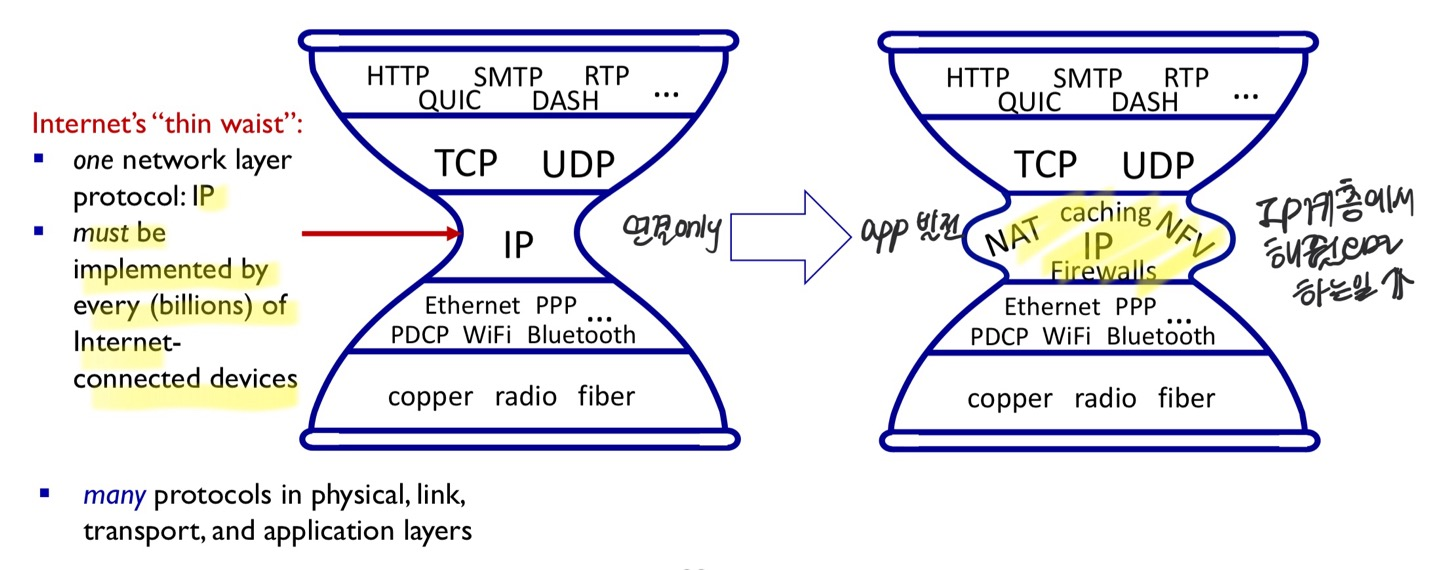
근데 점점 IP 계층에서 핸들링해주면 좋을 기능들을 막 추가하게 됨 ⇒ 합쳐서 middlebox라고 얘기함
특징
- After 40~50 years of IP deployment
- Middlebox : functions (NAT, Firewall, cache..) beyond forwarding
- NFV (Network Functions Virtualization) : middlebox functions can be implemented in cloud
- 네트워크 기능을 클라우드에 넣어 놔서 내 라우터에 있는 것처럼 동작 (실제 내 라우터에 있지는 않음)
- SDN과 NFV의 공통점은 IP 패킷을 처리(forwarding/dropping...)하는 장비와 어떻게 처리할 지를 계산하는 장비가 분리되어있다는 점.
- action 행동대장의 머리가 없다는 게 공통점 (brain과 body의 분리)
- 그러나 SDN은 제어 방식이 기존 라우터 (destination IP 주소만을 고려하여 forwarding만 실행)와 는 달리 중앙 제어로 할 수 있는 모든 기능을 포함한다.
- SDN is centralized control and configuration management often in private/public cloud
- NFV는 traditional routing 알고리즘 따름, 즉 결정하는 알고리즘은 그대로 destination-based-forwarding 임
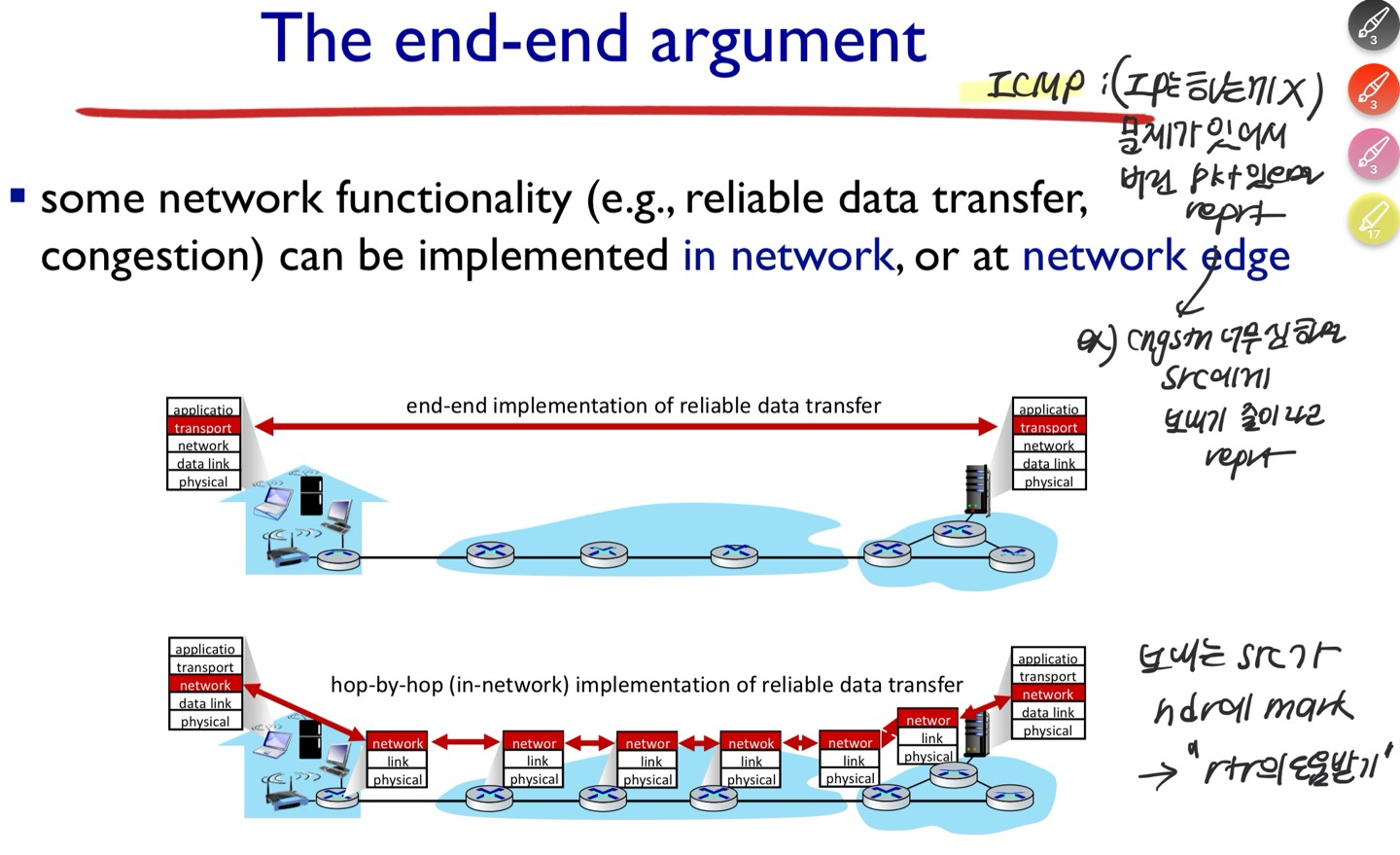
- ICMP
- 하다가 안되면 report라도 해라
- 옵션 중 source crinch 기능
- 라우터가 자기의 버퍼에 무리가 간다 했을 때, src 한테 ICMP가 좀 줄여라 알려줌
Keywords
- What are differences between IPv4 header and IPv6 header?
- What are the design objectives of IPv6? - Fast processing(forwarding) and Quality of service
- Transition technologies from IPv4 to IPv6
--- Dual stack : all nodes (router and hosts) have IPv4 and IPv6
--- NAT64 : translate address and protocol between IPv4 and IPv6
--- Tunneling : IPv6 packet is encapsulated into IPv4 payload
- Generalized forwarding in SDN networks : more general match + action
-- match : 2,3,4 layer header
-- action : load balancing, replacing address&port, selective dropping, deep inspection, etc as well as forwarding
'CS > Computer Network' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 5.1 Path selection (0) | 2023.12.12 |
|---|---|
| Network layer : Route aggregation & NAT (0) | 2023.12.09 |
| Network layer ; DHCP Protocol (0) | 2023.12.08 |
| Network Layer : Internet Protocol (0) | 2023.12.07 |
| Network Layer : The data Plane 총정리 (0) | 2023.12.06 |



